在Spring Cloud构建的微服务系统中,Ribbon作为服务消费者的负载均衡器,有两种使用方式,一种是和RestTemplate相结合,另一种是和Feign相结合。
Ribbon的负载均衡简单校验
编写控制器代码
/**
* @author 莫轩然
* @date 2020/5/26 16:17
*/
@RestController
public class RestTestController {
@Autowired
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
@GetMapping("/testRibbon")
public String testRibbon(){
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancerClient.choose("apo-outer-user");
return instance.getHost() + ":" + instance.getPort();
}
}
多次调用localhost:8082/testRibbon交替返回(本机启用两个apo-outer-user服务实例,分别为8083端口和8084端口,注册中心为Nacos Discovery)
localhost:8083
localhost:8084
由此我们可见,LoadBalancerClient实现了负载均衡的功能,但它具体是如何实现的呢?
源码分析Ribbon
我们跟踪LoadBalancerClient的源码,它是一个接口类,继承了ServiceInstanceChooser,它的实现类是RibbonLoadBalanceClient。
类关系图如下:
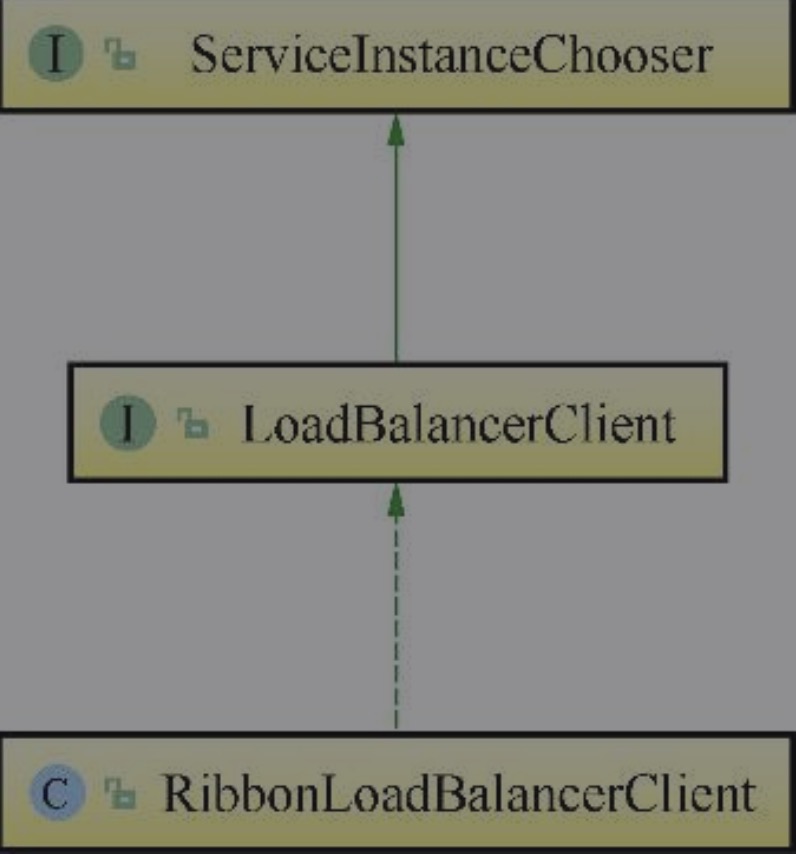
其中LoadBalancerClient下有3个方法,其中两个excute()方法,均用于执行请求,reconstructURI()用于重构Url,代码如下:
public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser {
/**
* 使用LoadBalancer中的ServiceInstance对指定服务执行请求
*/
<T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
/**
* 同上,只是参数不同
*/
<T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance,
LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
/**
* 创建带有真实主机和端口的适当URI,以供系统使用
*/
URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original);
}
ServiceInstanceChooser接口有一个方法用于根据serviceId获取ServiceInstance,即通过服务名来选择服务实例,代码如下:
public interface ServiceInstanceChooser {
ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId);
}
LoadBalancerClient的实现类为RibbonLoadBalancerClient,最终的负载均衡的请求处理由它来执行。 部分源码:
@Override
public ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId) {
return choose(serviceId, null);
}
/**
* New: Select a server using a 'key'.
* @param serviceId of the service to choose an instance for
* @param hint to specify the service instance
* @return the selected {@link ServiceInstance}
*/
public ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId, Object hint) {
Server server = getServer(getLoadBalancer(serviceId), hint);
if (server == null) {
return null;
}
return new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server, serviceId),
serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server));
}
其中choose方法用于选择具体服务实例,改方法通过getServer()方法去获取实例,最终交给ILoadBalancer类去选择服务实例。 源码如下:
public interface ILoadBalancer {
/**
* Initial list of servers.
* This API also serves to add additional ones at a later time
* The same logical server (host:port) could essentially be added multiple times
* (helpful in cases where you want to give more "weightage" perhaps ..)
*
* @param newServers new servers to add
*/
public void addServers(List<Server> newServers);
/**
* Choose a server from load balancer.
*
* @param key An object that the load balancer may use to determine which server to return. null if
* the load balancer does not use this parameter.
* @return server chosen
*/
public Server chooseServer(Object key);
/**
* To be called by the clients of the load balancer to notify that a Server is down
* else, the LB will think its still Alive until the next Ping cycle - potentially
* (assuming that the LB Impl does a ping)
*
* @param server Server to mark as down
*/
public void markServerDown(Server server);
/**
* @deprecated 2016-01-20 This method is deprecated in favor of the
* cleaner {@link #getReachableServers} (equivalent to availableOnly=true)
* and {@link #getAllServers} API (equivalent to availableOnly=false).
*
* Get the current list of servers.
*
* @param availableOnly if true, only live and available servers should be returned
*/
@Deprecated
public List<Server> getServerList(boolean availableOnly);
/**
* @return Only the servers that are up and reachable.
*/
public List<Server> getReachableServers();
/**
* @return All known servers, both reachable and unreachable.
*/
public List<Server> getAllServers();
}
其中,addServers()方法用于添加一个Server集合,chooseServer()方法用于根据key去获取Server,markServerDown()方法用于标记某个服务下线, getReachableServers()获取可用的Server集合,getAllServers()获取所有的Server集合,getServerList()被标记废弃。
ILoadBalancer的子类为BaseLoadBalancer,BaseLoadBalancer的实现类为DynamicServer-ListLoadBalancer,三者之间的关系如下图所示:
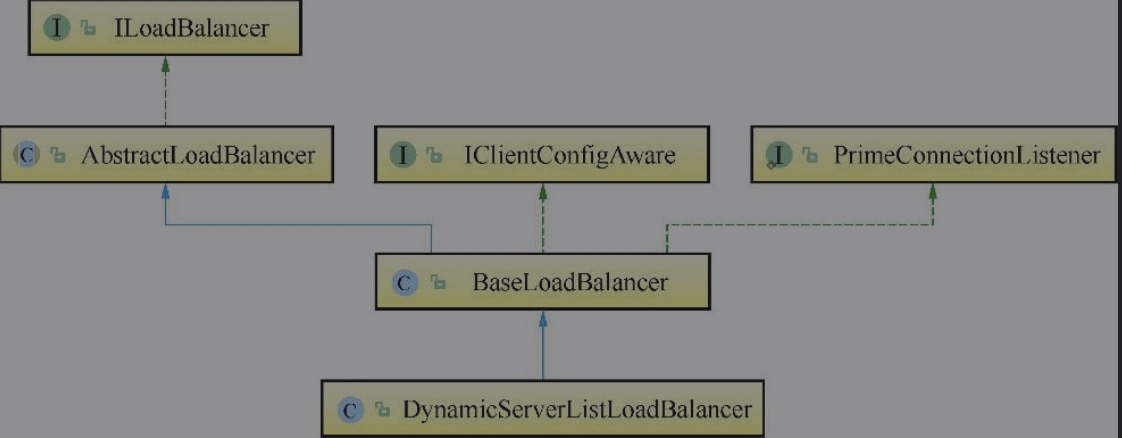
经过一步步追溯源码分析,到ServerList源码
public interface ServerList<T extends Server> {
public List<T> getInitialListOfServers();
/**
* Return updated list of servers. This is called say every 30 secs
* (configurable) by the Loadbalancer's Ping cycle
*
*/
public List<T> getUpdatedListOfServers();
}
就会发现NacosServerList实现了getUpdatedListOfServers方法,源码如下:
private List<NacosServer> getServers() {
try {
String group = this.discoveryProperties.getGroup();
List<Instance> instances = this.discoveryProperties.namingServiceInstance().selectInstances(this.serviceId, group, true);
return this.instancesToServerList(instances);
} catch (Exception var3) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can not get service instances from nacos, serviceId=" + this.serviceId, var3);
}
}
那么@LoadBalance注解就可以使用Ribbon的负载均衡呢? 在LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration类中,首先维护了一个被@LoadBalanced修饰的RestTemplate对象的List。在初始化的过程中, 通过调用customizer.customize(restTemplate)方法来给RestTemplate增加拦截器LoadBalancerInterceptor。 LoadBalancerInterceptor用于实时拦截,在LoadBalancerInterceptor中实现了负载均衡的方法。 LoadBalancerInterceptor类的拦截方法的代码如下:
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body,
final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
final URI originalUri = request.getURI();
String serviceName = originalUri.getHost();
Assert.state(serviceName != null,
"Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri);
return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName,
this.requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution));
}
综上所述,Ribbon的负载均衡主要是通过LoadBalancerClient来实现的,而LoadBalancerClient具体交给了ILoadBalancer来处理, ILoadBalancer通过配置IRule、IPing等,默认每10秒向DiscoveryClient发送一次“ping”, 进而检查是否需要更新服务的注册列表信息。最后,在得到服务注册列表信息后,ILoadBalancer根据IRule的策略进行负载均衡。
而RestTemplate加上@LoadBalance注解后,在远程调度时能够负载均衡,主要是维护了一个被@LoadBalance注解的RestTemplate列表, 并给该列表中的RestTemplate对象添加了拦截器。在拦截器的方法中,将远程调度方法交给了Ribbon的负载均衡器LoadBalancerClient去处理, 从而达到了负载均衡的目的。